Windows Task Manager (Basics)
Windows Task Manager is a powerful application that is part of the Windows OS. It gives valuable information and insight into system resource usage. This group of articles details each aspect of Task Manager, how to perform the functions, and then use the results to troubleshoot.
This article discusses how to access Task Manager in Windows 10/11.
Accessing Task Manager
There are several methods to open the Task Manager:
- Ctrl + Alt + Del or Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Use search for “Task Manager”
- Right Click on Start and Select “Task Manager”
- Right-click the taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
The first time Task Manager is opened, the default screen “Processes” will be displayed. To change the default in Windows 10 click on “Options” in the top menu and select “Set default tab”.
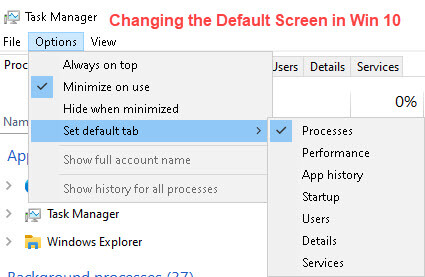
Difference Between Versions
Windows 10 opens in minimized view. Click on “More details” to open the full view. You may change this by removing the check mark in Options> Minimize on use. The full menu will then become the default view.
The top of the screen starts with a small set of menu items:
- File: (Run New Task) – (Exit)
- Options: (Always on top) – (Minimize on use) – (Hide when minimized) – (Set Default tab) – (Show Full account name) – (Show history for all processes)
- View: (Refresh now) – (Update speed) – (Group by type) – (Expand all) – (Collapse all)
Windows 11 does not include the menu but instead gives quicker access to “Run New Task, and End Task. A new feature is Efficiency mode:
Tabs Vs Icons
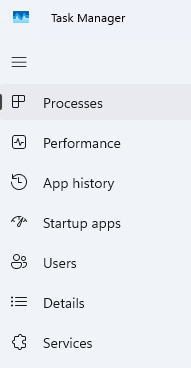
Below the Menu, Windows 10 displays tabs used to navigate to available options. 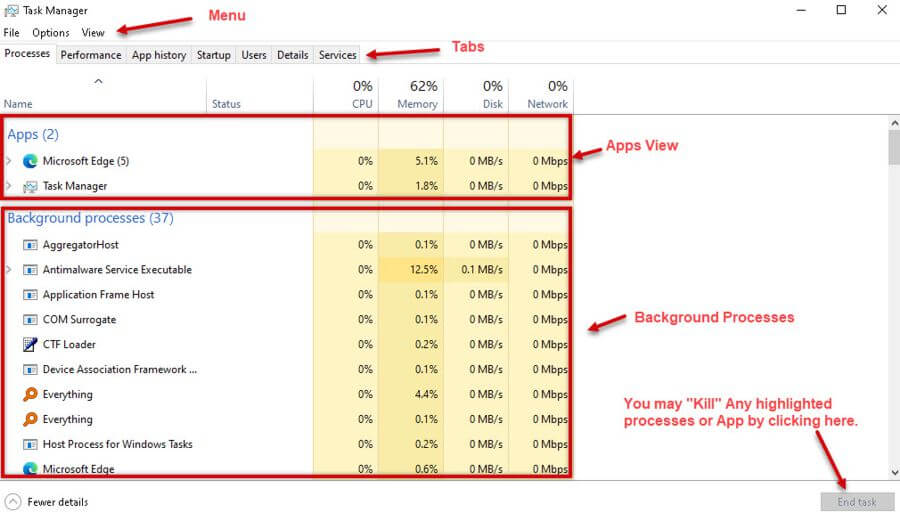
Windows 11 shows them as a list of Icons to the left of the screen but both have the same options:
- Processes: A list of all running apps and processes
- Performance: This is an overview of your resources displayed in a graph format:
- CPU
- Memory
- Disk(s)
- Ethernet
- Open Resource Monitor: Click to open a new screen showing your resources in detail
- App History: A view of processes showing resources over time
- Startup: A list of startup apps that can be enabled or disabled
- Users: Processes used by each user
- Details: Additional information for each of the running processes
- Services: A list of all services on your OS including their Name, PID, Brief Description, Status as either Stopped or Running, and which group they belong to:
- Open Services: An option to open Services from the Microsoft Management Console. It contains a better description of each service and the Startup Type used. You may use this screen to Start, stop, and configure Windows Services.
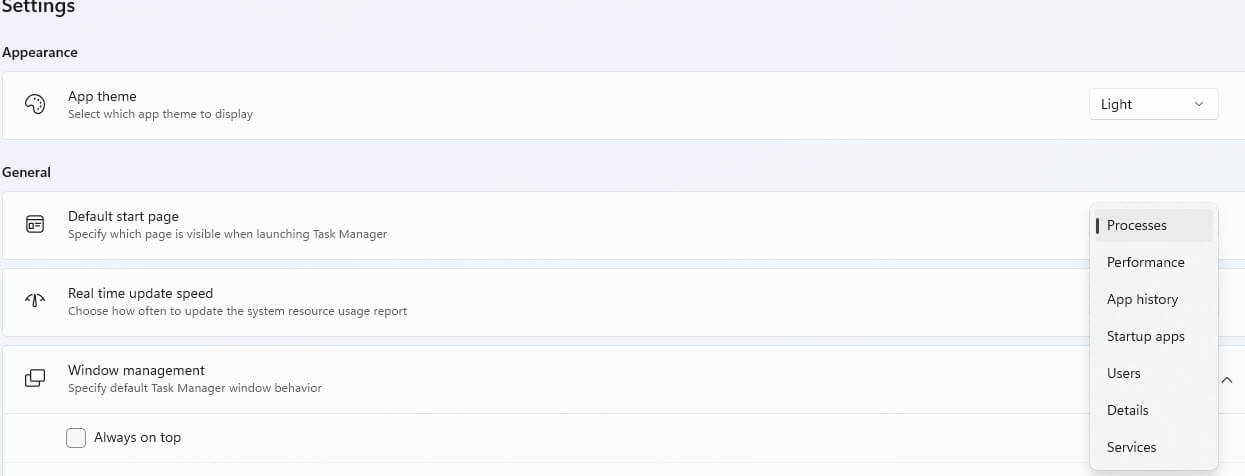
Settings In Windows 11
Windows 11 includes “Settings”, a Gear icon located at the bottom, below the Services Icon that gives you several new options:
- Appearance
- Change the App theme
- General
- Change the Default Page
- Real-Time Update Speed – Set how fast the resource usage is updated
- Windows Management – Define how the Task Manager Window should behave. Always on top, Hide, etc
- Other Options include displaying the full account name, viewing process history, and determining if the Efficiency mode needs permission
- Advanced – Live kernel memory dumps – Dumps create a snapshot of kernel memory without restarting the computer. You may troubleshoot situations while keeping the OS operational
- Abort if insufficient memory: When selected, the live dump process stops if memory is insufficient. This minimizes the impact of system responsiveness
- Capture Hypervisor pages: Chose to capture memory regions used by the hypervisor used to support Hyper-V and virtual machines
- Include nonessential pages: Choose to include or exclude nonessential hypervisor memory pages
- Capture User Pages: Enable this if your troubleshooting requires user-mode memory
- Reset Settings: Resets to default settings
- Send Feedback: Only for Feedback Hub users. Sign in and give your feedback in a preformatted form
Summary
This is an overview of the basic Task Manager functions and some differences implemented in Windows 11.
—