Performance View
Performance, the second tab in the Task Manager is the only tab that is laid out differently between versions. Both have the same functionality, but the layout of the screens is just different enough to believe one option is missing. In Windows 10 the “Open Resource Monitor” option is always visible at the bottom of the screen. In Windows 11 however, it is hidden as an option behind the 3 dots (ellipsis) in the upper right corner. Getting there may be slightly different, but both have the same abilities.
Performance Tab
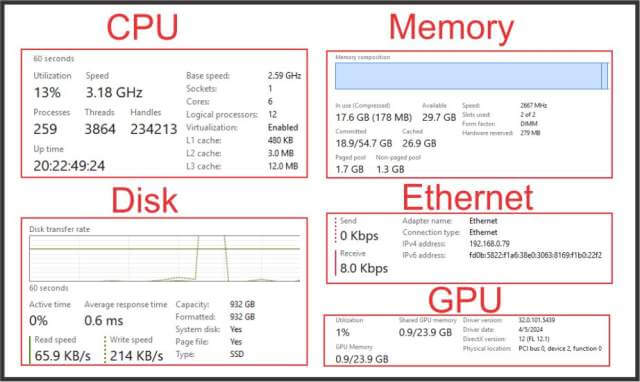
The Performance tab gives us an overview of the four main resources of your system. CPU, Memory, Disk and Network in Windows 10. Windows 11 also includes the GPU as a resource. The left pane contains a very small graphic chart of each resource.
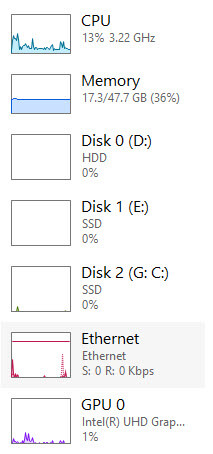
The number of graphs visible depends on several factors, the number of CPUs you have, the number of Disk Drives in use and the number if any of GPUs. The right pane contains a larger view of the resource selected in the left pane. In the image below each spike indicates traffic on my ethernet. 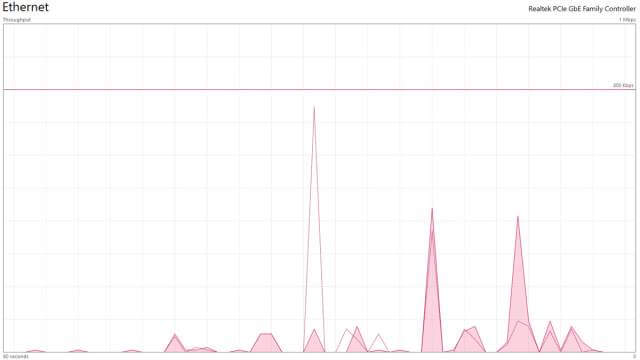
This enlarged view of the resource at the right provides additional information to help you understand the features of the resource. It is a basic overview of a resource and the information at the bottom of the chart is different for each resource. The available data changes to information that is meaningful to that resource.
Summary
The Performance Tab is good for an overview of resources, and you may quickly spot an issue, but it does not provide the detail and breakdown given in the Resource Monitor View discussed in the next article. Us it to see any obvious issues like if you are coming to the maximum use of Memory, Slow disk read/writes and excess Ethernet traffic. If you do see an issue, you can then use the Resource Monitor view to get the detail you will need to troubleshoot a problem.
—