Users, Details, Services
Users
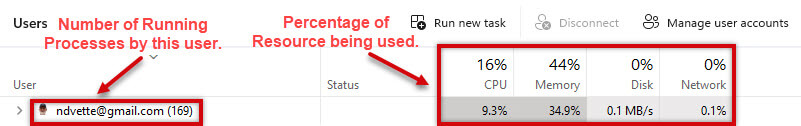
The fifth tab in Task Manager is Users. The first column lists all user accounts currently signed in. If you expand the name of a user, you will get a list of the processes equal to the number shown to the right of their name. The columns show the system resources used by each user.
As with previous screens, the headers can be moved left and right, and additional columns added. This screen can be useful to determine if some users are using more resources than they should. It is not very helpful if only one user is listed. Any description is already provided in the previous tabs.
Details
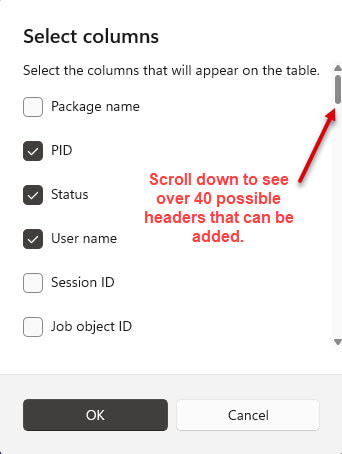
As the saying goes, it is all in the details and this screen has a whopping 46 possible headers in Windows 10 and 48 in Windows 11.
You can study any running process to better understand it. With that many ways to view each process, you analyze a process using several filters. The large number of column headers is too long to put in an article of this scope. But if you want to look at a process in several different ways, you can do it here.
Services
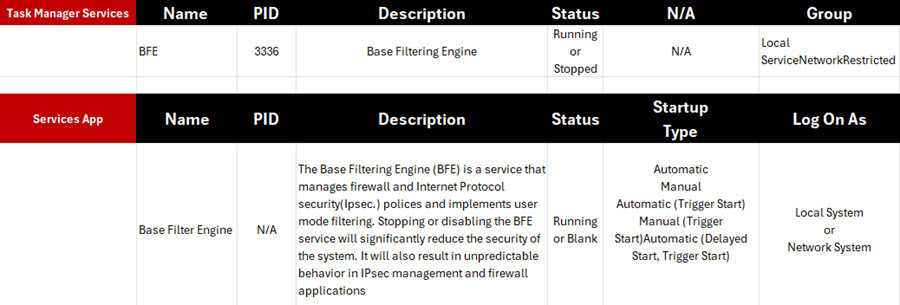
The final tab in Task Manager is Services. I have never been sure why it was included in this application because a much more detailed version can be seen by typing “services” in the search bar and opening the Services app. The Process ID (PID) is the only significant label available in Task Manager but not in the Services app. If you want to investigate services, I highly recommend not using the one provided in Task Manager but using the Services app.
The description alone is reason enough to use the Services app. As an example, if you wanted to look up the service “Base Filtering Engine”, here are the differences between Task Manager (services) and the Services App.
Use It To Detect Malware
Task Manager and all the screens available are an incredible troubleshooting tool for detecting malware. Look for any processes with an unreasonably high amount of memory or CPU usage. Look for processes with unfamiliar names. Right-click on any process and use the Search Online option to understand what the process is and if it should be on your PC. Check if the process is being run from an unexpected location. Use the Command Line feature to see how your process started and from where.
In the Users Tab, ensure you know every user accessing your PC and that processes are not being used by unauthorized users. Using the Resource Monitor you can check every process that is using your Network. Not only how much resource it uses but if you are the owner of that process. If you see traffic that is not yours, it probably means you are hacked and someone else is accessing the network. Again, right-click on the name of any process and use the online feature to investigate what the app is and why it is running on your machine.
Summary
The great thing about using Task Manager is that it can act as a teacher, helping you understand the way your resources are used. Have fun and experiment; it is a very safe application. Simply stated, I think the Task Manager is the most powerful built-in tool in Windows and an easy tool for the average user to experiment with.
—

Very informative Jim. A refresher course into the Task Manager, and it is included with the o/s at no extra cost. Wish I had this information years ago. Would have saved me countless hours figuring out some of the hidden features and how to use them, but thank you for helping others, Mindblower!
Thanks for the feedback. Appreciated